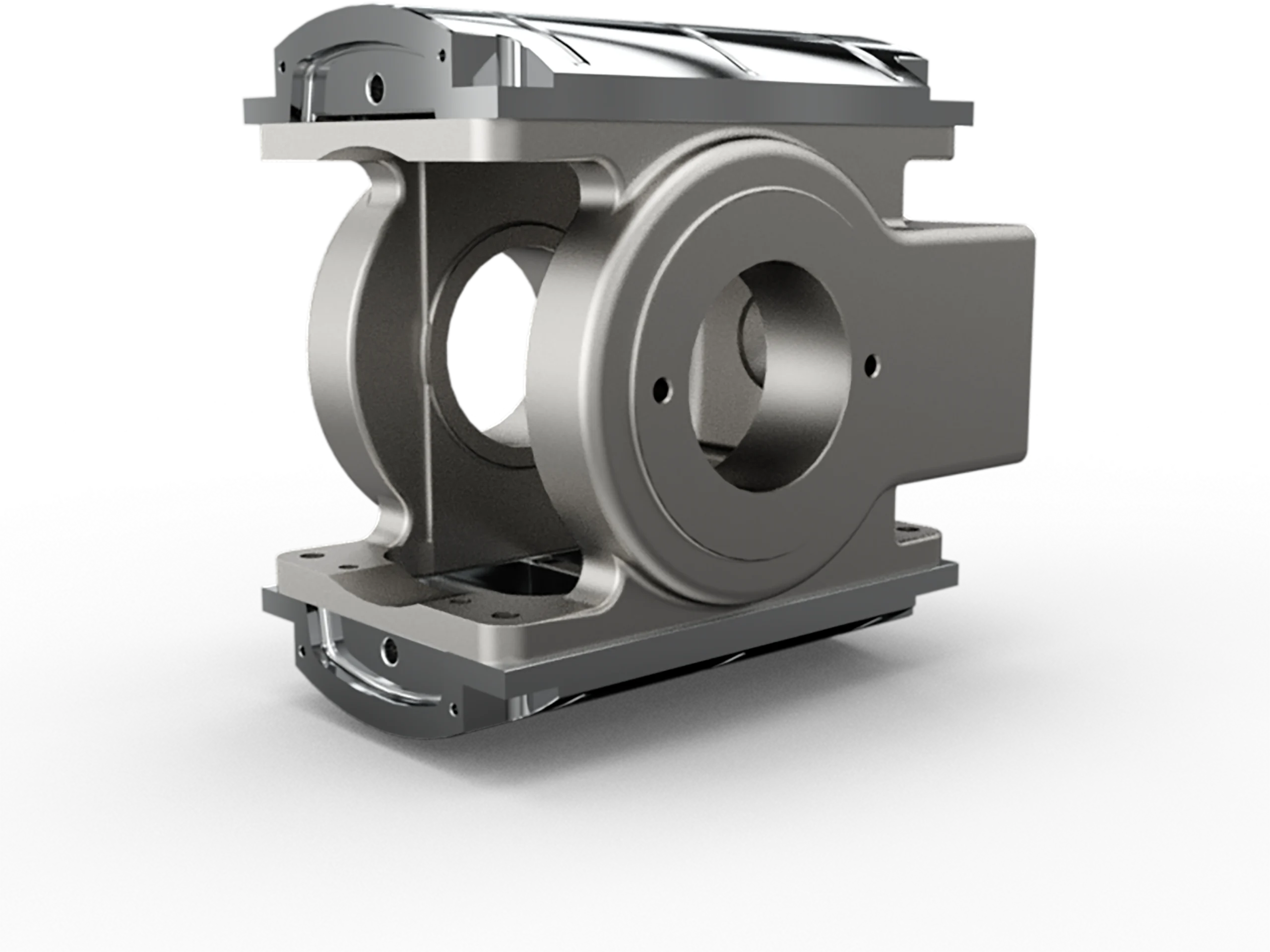
Crosshead, guide & guide shoe
Crosshead, guide & guide shoe
Globagon manufactures parts that play a critical role in maintaining alignment and reducing wear in reciprocating compressors.
The crosshead absorbs and transfers dynamic loads from the piston rod to the connecting rod, ensuring smooth force transmission under high mechanical stress. Guide shoes are precisely machined to control lateral movement, minimizing friction and extending component life. The surfaces provide stable support throughout the stroke, contributing to consistent, vibration-free operation.
Each component is available in a range of materials and configurations to suit specific frame designs, lubrication systems, and operating conditions.
We can also do Babbitt coating according to customer specifications.
Working Principle
The crosshead is a critical component positioned between the piston rod and the connecting rod, designed to prevent lateral forces from being transmitted to the piston.
Due to the frequent failures of crossheads caused by loads exceeding standard limits, Globagon’s team has implemented corrective actions in the redesign and manufacturing of this component.
While maintaining standard weight and dimensions, we have selected a high-performance alloy with superior structural integrity and work potential. This ensures reliable compressor performance and enhanced component durability under demanding operating conditions.
The guide and guide shoe are essential for stabilizing the crosshead’s motion. As the connecting rod operates, it generates lateral forces due to its angled movement. The guide system absorbs these forces and ensures that only linear motion is transmitted to the piston rod. This contributes to smoother operation, reduced wear on piston rings and cylinder walls, and longer component life.
The system typically consists of a guide rail—either integrated into or bolted onto the compressor frame—and a pair of guide plates that form a precise channel for the guide shoe. The shoe moves up and down within this channel in sync with the piston stroke, keeping the entire mechanism aligned and efficient throughout the compression cycle.
Display
Why Crosshead, Guide and Guide Shoes are important
In the world of reciprocating compressors, where precision and durability are paramount, the crosshead and its associated guide system often serve as unsung heroes. While these components may appear relatively straightforward in form, their role is critical in ensuring the mechanical integrity and performance consistency of the compressor. For engineers, technicians, and operations teams working on heavy-duty machinery, the reliability of these parts is not just a design concern—it’s a daily operational reality.
At its core, the crosshead acts as a mechanical buffer—positioned precisely between the piston rod and the connecting rod—to isolate the piston from side loads generated by the rotating crankshaft. In theory, the motion of a piston in a reciprocating compressor should be perfectly linear. But in practice, the dynamic forces at play, particularly the angled motion of the connecting rod, introduce lateral loads that, if unmitigated, can cause significant wear or even catastrophic failure in the piston-cylinder assembly.
Crossheads absorb and redirect these forces, translating the connecting rod’s angled motion into a clean, linear stroke for the piston rod. Without this intermediary, the piston itself would be forced to bear these side loads directly—an unsustainable condition that would accelerate wear on piston rings, score cylinder walls, and compromise sealing effectiveness. In high-speed or high-pressure compressors, this problem only intensifies, making the integrity of the crosshead system a non-negotiable engineering requirement.
This is precisely why Globagon’s decision to redesign and reinforce the crosshead is both timely and technically astute. Field data from various operational environments had made it clear: while the existing crosshead design met standard specifications, it was not always capable of withstanding the higher dynamic loads seen in increasingly demanding industrial applications. Failures—though not always catastrophic—were occurring too frequently, prompting a deeper investigation.
The outcome was not a complete overhaul, but a targeted redesign rooted in real-world performance feedback. By maintaining the crosshead’s standard geometry and weight—thus ensuring compatibility with existing compressor setups—Globagon focused instead on material science. The newly selected alloy boasts enhanced fatigue resistance, better thermal tolerance, and higher yield strength. These characteristics translate directly to longer service life, fewer unexpected failures, and lower maintenance costs.
But the crosshead alone does not bear the full responsibility of ensuring smooth operation. Equally vital are the guides and guide shoes, which provide directional stability to the moving parts. Imagine the crosshead as a train car—without rails, its movement would be erratic and dangerous. The guide system serves as those rails, ensuring that the crosshead only travels in the intended path.
Typically, the guide system is composed of fixed rails or channels—machined into or bolted onto the compressor frame—and matched with guide plates that constrain the movement of the guide shoe. The guide shoe, in turn, is often made from a wear-resistant material, and it slides with tight tolerances inside the channel to maintain strict alignment.
This may sound like a simple mechanical arrangement, but in reality, it requires a delicate balance of precision engineering and material science. Even small deviations in alignment or unexpected wear on the guide surfaces can introduce vibrations, reduce efficiency, and increase stress on all associated components. That’s why proper lubrication, precise machining, and robust materials are all essential in ensuring the long-term performance of the guide system.
Moreover, the interaction between the crosshead and the guide system is dynamic. As the compressor runs, thermal expansion, fluctuating loads, and lubricant condition all affect how smoothly these components operate. That’s why Globagon has also looked at refining the surface finish of the guide shoes and enhancing the lubrication channels to ensure consistent oil film distribution during operation. These small adjustments collectively yield significant gains in overall reliability and efficiency.
From a human perspective—whether you’re an operator in a remote oilfield or a maintenance engineer in a chemical plant—the importance of these components often becomes clear only when something goes wrong. A seized crosshead or worn guide shoe can lead to downtime that costs thousands of dollars per hour. That’s why preventative design and quality manufacturing are not just about engineering excellence—they’re about minimizing risk and maximizing uptime for people who depend on these machines.
Globagon’s approach reflects a growing trend in industrial machinery design: listening to field experience, using data-driven decision-making, and making incremental, targeted improvements that offer real-world value. While the redesign of the crosshead might not be revolutionary, it is rooted in respect for the work these machines do and the people who keep them running.
By combining high-performance materials with thoughtful engineering, and by focusing equally on the mechanical system and its human context, Globagon continues to raise the standard for reliability and operational excellence in compressor design.