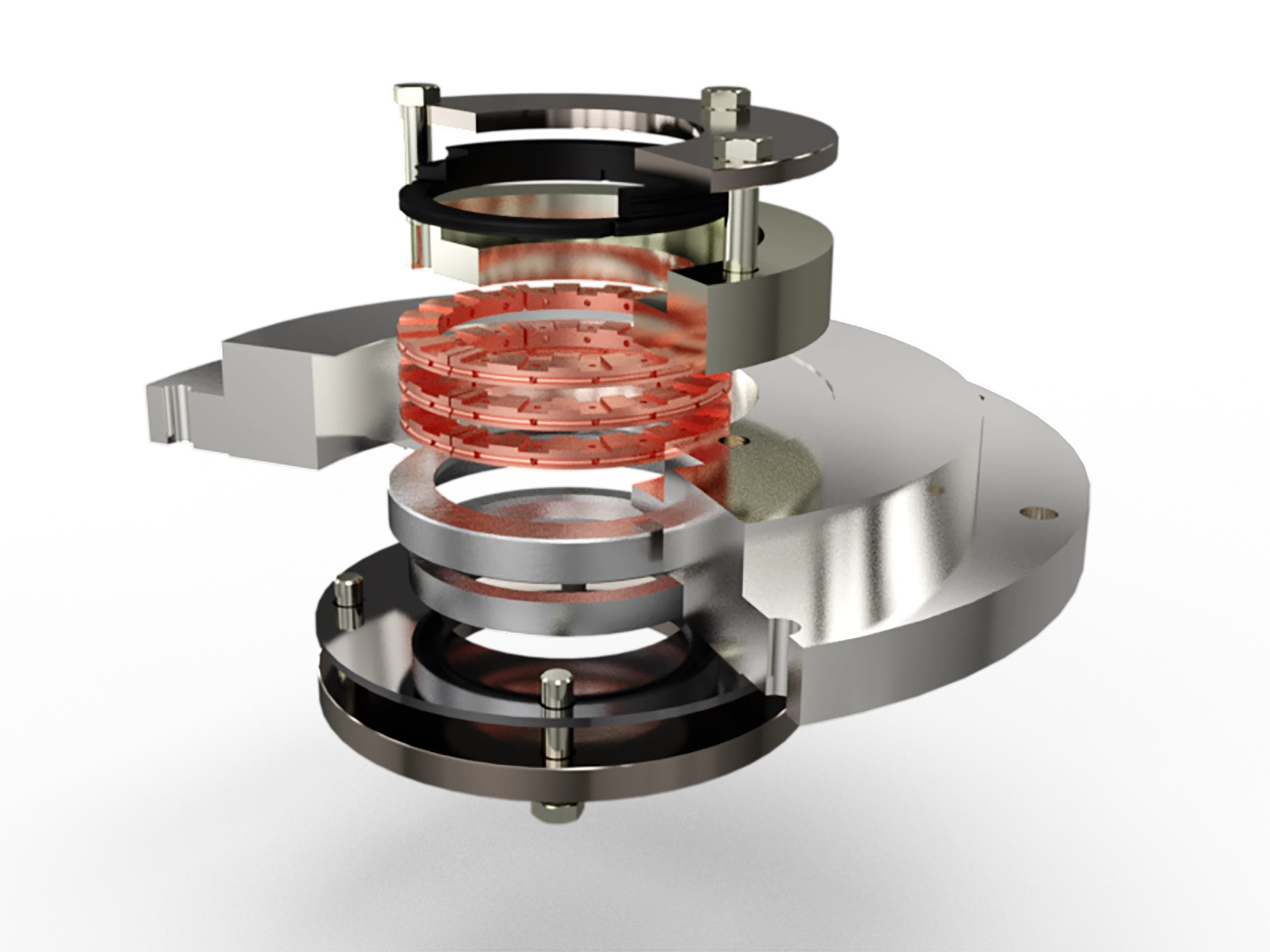
Oil Wipers
Oil Wipers
Globagon oil wiper rings are designed to use in reciprocating compressors with horizontal, vertical, or angled configurations. Their primary function is to effectively remove excess oil from the piston rod.
These rings can be combined with other ring types to provide added benefits such as lateral oil scraping and improved sealing performance. Our designs utilize Finite Element Analysis to precisely position cavity holes for optimized oil control, while also considering key performance factors including chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength.
Each product is manufactured to either OEM specifications or customized dimensions provided by the client, ensuring full compliance with industry standards and exceptional build quality.
Developed with a comprehensive understanding of compressor operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, gas composition, and lubrication systems—Globagon oil wiper rings are produced from high quality materials to ensure reliable, long-lasting performance in even the most demanding environments.
Working Principle
Oil Wipers
Oil wiper packing plays a key role in improving compressor reliability by keeping lubricating oil confined to where it’s needed and preventing contamination of downstream components and processes. In both lubricated and non-lubricated compressors, properly functioning wiper rings reduce oil consumption, lower operational costs, and help prevent environmental leakage.
By scraping excess oil from the piston rod during each stroke, oil wipers prevent crankcase oil loss, stop oil from reaching the pressure packing and cylinder in non-lube systems, and block cylinder oil from migrating back into the crankcase.
Typically located near the crosshead assembly, wiper rings also limit the unintended flow of oil caused by the pumping action of the reciprocating rod. To achieve optimal performance, they must remove oil uniformly around the entire rod circumference and incorporate a drain profile suited to the specific compressor design.
Display
What are Oil Wipers?
Oil wipers, also known as oil wiper packings or wiper rings, are essential components in reciprocating compressors that ensure reliable and efficient operation by managing the distribution of lubricating oil. Their primary role is to prevent oil from escaping its intended lubrication zone and to stop contamination of downstream equipment and processes. While they may seem like a small part of the overall compressor design, their function is critical to maintaining system integrity, reducing oil consumption, and extending equipment life.
Function and Importance
The operation of a reciprocating compressor involves continuous movement of the piston rod between the crankcase and the cylinder. This motion requires lubrication at the crosshead and crankcase ends, but the same oil must not be allowed to reach the compression chamber or downstream process gas. Oil wipers provide the barrier that makes this separation possible. By scraping excess oil from the piston rod during each stroke, they return it to the crankcase or designated drain path, ensuring that only the correct amount of lubrication is retained on the rod surface.
In lubricated compressors, wipers help maintain proper lubrication levels while preventing excessive oil carryover. In non-lubricated (non-lube) compressors, they play an even more crucial role: stopping crankcase oil from migrating toward the pressure packing and cylinder, where even small amounts of oil contamination can compromise gas purity, damage equipment, or affect end-product quality.
Performance Benefits
A properly designed and maintained oil wiper system provides several performance advantages:
Reduced Oil Consumption – By preventing oil loss, wipers reduce the frequency of lubricant replenishment, lowering operational costs.
Improved Reliability – Limiting oil leakage helps keep critical components cleaner and prevents premature wear caused by oil contamination.
Environmental Protection – Effective wipers minimize the possibility of oil leakage into the atmosphere or surrounding equipment, supporting compliance with environmental standards.
Process Integrity – In applications where gas purity is essential, such as in chemical, petrochemical, and food-grade industries, oil wipers prevent unwanted hydrocarbons from contaminating the gas stream.
Design Considerations
The effectiveness of an oil wiper depends on its ability to uniformly remove oil from the piston rod around the entire circumference. Uneven wiping can leave streaks of oil that bypass the system and cause carryover into the cylinder or crosshead. To achieve this, wiper rings are manufactured to tight tolerances and often include multiple segments that can flex to accommodate slight misalignments or rod eccentricities.
Another key factor in design is the drain profile. Oil removed by the wiper must have a clear path back to the crankcase or a separate drain system. Without proper drainage, oil can accumulate behind the wiper, eventually being forced past the packing due to pressure buildup or rod motion. Compressor manufacturers often tailor the drain profile to the specific machine design, ensuring efficient removal of collected oil.
Material selection is also critical. Wipers are exposed to continuous friction, pressure pulsations, and the chemical environment of the process gas. As a result, they are typically made from durable materials such as bronze, filled PTFE, or composite alloys that provide both wear resistance and sealing performance. The choice depends on whether the compressor is lubricated, non-lubricated, or handling corrosive gases.
Maintenance and Reliability
Even the best-designed oil wipers will degrade over time due to wear, thermal cycling, and exposure to process conditions. Regular inspection and timely replacement are essential to sustaining performance. Signs of wiper failure include increased oil consumption, oil contamination of the cylinder, or visible oil leakage around the rod.
Maintenance intervals depend on compressor duty, operating conditions, and lubricant type. For critical applications, predictive maintenance techniques—such as monitoring oil consumption rates or using rod drop measurement systems—can help detect early signs of wiper wear. Proactive replacement prevents secondary damage to pressure packing, cylinders, and crossheads.
Role in System Efficiency
By preventing unnecessary oil migration, oil wipers help maintain a clean, efficient compressor system. Reduced oil loss translates directly to lower lubrication costs and fewer environmental risks. Additionally, preventing oil from reaching areas where it does not belong avoids costly downtime and repairs. In non-lube compressors, their role is indispensable, as they preserve gas quality and system cleanliness.
In summary, oil wiper packings are far more than simple sealing elements. They are precision-engineered components that directly influence compressor efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. Whether in lubricated or non-lubricated machines, their ability to control oil flow ensures long-term performance and protects both equipment and processes from the damaging effects of oil contamination.